Over two years have passed since Congress passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), and hundreds of substantial infrastructure improvement projects are already in full swing across the country. Highlighted below are a few of the top-funded projects underway in Connecticut, New Hampshire, Maine, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
- $1.4 billion for transportation investments in roads, bridges, public transit, ports, and airports, as well as electric school and transit buses, EV charging, and more.
- $155 million for grants, rebates, and other initiatives to accelerate the deployment of clean energy, clean buildings, and clean manufacturing. This is not inclusive of the clean energy tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- $72.7 million to make communities more resilient to climate change and other threats.
- $158.3 million to provide clean water across Rhode Island and improve water infrastructure. This includes $57 million dedicated to lead pipe and service line replacement.
IIJA Funding: $82.5 million
Construction Start Date: 2020
End Date: 2024
In the 1960s, the Pell Bridge and Interchange were completed; however, the Route 138 northbound approach was never completed, which would have connected Newport to Route 24 in Portsmouth, Rhode Island. Then between 2001 through 2008, the Rhode Island Office of Statewide Planning identified the Aquidneck Island Travel Corridor as a major travel corridor of statewide significance. Long-range goals were established to the year 2020 including: protecting the open space and scenic vistas of ocean and agricultural lands by confining mixed-use development to designated growth centers, and providing transportation alternatives and network connections including expanded ferry service, increased bus schedules, improved bicycle and pedestrian circulation, and Park & Rides that provide a safer network for all modes of transportation.
RIPTA Newport-Middletown Garage and Bus Electrification
IIJA Funding: $22.4 million
Construction Start Date: 2023
End Date: Spring 2026

| Your local Trimble Construction Division dealer |
|---|
| SITECH Southwest |
| SITECH Northwest |
| SITECH Rocky Mountain |
| SITECH Southwest |
| SITECH Northwest |
| SITECH Rocky Mountain |
With the electrification of one entire route complete, the next major step toward broader statewide fleet transition is the electrification of the Aquidneck Island fleet and support operations. This project involves the full electrification of Newport/Middletown Garage and the introduction of 25 battery-electric buses that will operate on Routes 63, 64, 67, 68, and 69. The garage will have its electrical systems upgraded and chargers installed to provide power to the vehicles. Additional charging infrastructure is expected to be installed at the Newport Transportation Center.
“Battery-powered buses will soon be the cleanest, most efficient way to get around Aquidneck Island,” said U.S. Senator Sheldon Whitehouse, a Newport resident and senior member of the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee. “This is a win for passengers, who will get to ride on state-of-the-art electric buses, and for our environment.”
Providence I-95 Viaduct Northbound
IIJA Funding: $12.4 million
Construction Start Date: 2020
End Date: 2025
This project will replace the 1,295-foot-long northbound section of the Providence Viaduct Bridge which carries I-95 over numerous local roads and highway ramps, Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, and the Woonasquatucket River. This section of I-95 carries more than 220,000 vehicles per day. It is the busiest section of I-95 in Rhode Island and one of the most heavily trafficked highway bridges on the East Coast. The project includes the construction of a new collector-distributor road along the right side of the interstate. This eliminates the weaving conflicts and congestion that plague the segment of I-95 Northbound from the 6/10 Connector and Downtown on-ramps to the Route 146/State Offices interchange.
Engineering and Construction of Providence’s Urban Trail Network
IIJA Funding: $27.2 million
Construction Start Date: January 2023
The City of Providence will advance engineering and systemic construction of the city’s Urban Trail Network. This project will create last-mile connections to residential, employment, and cultural activity centers between the city’s 25 neighborhoods while significantly reducing fatal and serious crashes for vulnerable road users. The trails are a combination of on-road and road-adjacent protected bicycle lanes and shared-use trails, neighborhood greenways on low volume streets, and off-road shared-use paths.
“This is a smart investment in preventing traffic accidents, improving our streets, and connecting neighborhoods,” said U.S. Senator Jack Reed, a senior member of the Appropriations Subcommittee on Transportation, Housing, and Urban Development. “This federal funding will help Providence reach its infrastructure and mobility goals and make our streets safer and more efficient.”
- $5.4 billion for transportation investments in roads, bridges, public transit, ports, and airports, as well as electric school and transit buses, electric vehicle (EV) charging, and more.
- $173.7 million for grants, rebates, and other initiatives to accelerate the deployment of clean energy, clean buildings, and clean manufacturing. This is not inclusive of the clean energy tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- $95.7 million to make communities more resilient to climate change and other threats.
- $192.8 million to provide clean water across Connecticut and improve water infrastructure. This includes $68.3 million dedicated to lead pipe and service line replacement.
IIJA Funding: $826.6 million
Construction Start Date: 2024
End Date: 2031
Constructed in 1907, the 1,500-foot-long Connecticut River Bridge comprises 10 spans including a 160-foot-long drawspan. The replacement project will involve building a two-track, electrified, and resilient movable bridge structure equipped with new track, signal, catenary, power, communication, controls, and security features. The new bridge structure is expected to have a design life of 150 years. The bridge replacement will allow for better reliability and decreased delays for travelers due to trains traveling on more modern infrastructure.
“When this new bridge is finished, rail traffic will be safer and faster for passengers on the Northeast Corridor-Acela Express, Northeast Regional, and Shoreline East, as well as freight traffic,” U.S. Representative Joe Courtney said. “This is a generational investment for the most heavily traveled rail system in America that will pay dividends for decades to come.”
WALK Bridge Replacement
IIJA Funding: $465 million
Construction Start Date: 2023
End Date: 2029
The WALK Bridge Program comprises several inter-related rail and infrastructure projects in Norwalk, Connecticut. The centerpiece project replaces the Norwalk River Railroad Bridge, known locally as the WALK Bridge. The WALK Bridge is a four-track railroad bridge that serves as a critical link in the busiest rail corridor in the nation, the Northeast Corridor (NEC). Replacement of the 127-year-old WALK Bridge will strengthen commuter rail safety, enhance commuting reliability, and increase operational efficiency along the New Haven Line and Northeast Corridor.
“After years in Congress fighting for federal money to upgrade and replace Norwalk’s WALK Bridge and the Westport Saugatuck River Bridge, I am elated to have helped secure nearly $500 million to bring these projects across the finish line,” U.S. Representative Jim Himes said. “I spend much of my time as a representative thinking about how to modernize the rail systems and bridges in our community, but the best part about receiving a grant like this is knowing that eventually my constituents won’t have to think about infrastructure at all.”
Devon Bridge Replacement
IIJA Funding: $245.92 million
Construction Start Date: 2024
End Date: 2035
This project will provide a safe and reliable bridge crossing for rail over the river as well as marine navigation under the rail. State representatives said Devon Bridge serves as a critical transportation link between Stamford and New Haven on MNR’s New Haven Line and between New York and Boston on Amtrak’s NEC and carries 6,300 passengers every day.
- $934.3 million for transportation investments in roads, bridges, public transit, ports, and airports, as well as electric school and transit buses, EV charging, and more.
- $105.7 million for grants, rebates, and other initiatives to accelerate the deployment of clean energy, clean buildings, and clean manufacturing. This is not inclusive of the clean energy tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- $27.5 million to make communities more resilient to climate change and other threats.
- $172.1 million to provide clean water across New Hampshire and improve water infrastructure. This includes $57 million dedicated to lead pipe and service line replacement.
IIJA Funding: $34.9 million
Construction Start Date: Summer 2022
End Date: Fall 2024
The Exit 4A project will construct a new interchange on I-93 in Londonderry, about a mile north of Exit 4. The new interchange will provide access to the east side of I-93 via a new connector road (to be known as Old Rum Trail) to its connection with Folsom Road in Derry. The work on I-93 is approximately 1 mile long. This project involves constructing a new road, Old Rum Trail, between the interchange in Londonderry and Folsom Road in Derry. The project corridor continues to the east with upgrades to Folsom Road, Tsienneto Road, and NH Route 102 (Chester Road). The project also includes multimodal improvements related to the Derry Rail Trail corridor connectivity, added sidewalks, and widened shoulders for bicycle use. This project also includes stormwater system improvements to protect local water resources.
I-93 Northbound Bridge Preservation
IIJA Funding: $12.8 million
Construction Start Date: April 2024
End Date: October 2025
This project will address preservation needs on five northbound I-93 bridges — the U.S. 3 bridge, Wellington Road bridge, Stevens Pond bridge, Stack bridge, and Bridge Street bridge — between Exit 6 in Manchester and Exit 9 in Hookset. The work will include replacement of bridge pavement and membrane waterproofing; repairs to concrete decks, bridge curbs, and bridge rails; and replacement of bridge deck joints.
Errol NH16 Widening and Rehabilitation
IIJA Funding: $8.6 million
Construction Start Date: 2023
The New Hampshire Department of Transportation will realign, reconstruct, and operate an approximately 1.3-mile segment of New Hampshire Route 16 (NH Rt 16) in the town of Cambridge, Coös County, New Hampshire. The activity area begins approximately 1,000 feet east of the town line in Dummer-Cambridge, New Hampshire, runs west and generally parallel to the Androscoggin River, and is approximately 17.5 miles north of Berlin, New Hampshire. The activity realigns NH Rt 16 west and away from the Androscoggin River from 15 feet to 385 feet; results in 225,953 square feet of permanent impacts and 17,032 square feet of temporary impacts to wetlands; and results in 568 linear feet of permanent and 225 linear feet of temporary impacts to stream channels.
Renewing Berlin with Renewable Energy
IIJA Funding: $19.5 million
The project will include the rehabilitation of roads, sidewalks, and municipal parking areas, coupled with the installation of a snow-melt system in downtown Berlin. It includes an improved pedestrian crosswalk with bump-out curbs, high-visibility crosswalk markings, ADA-compliant sidewalks, and new street trees. The project will improve access to the downtown area for residents and visitors during winter. The improved streetscape without snow and ice during winter will reduce vehicle crashes, decrease pedestrian slips and falls, and improve access for residents and visitors to services in downtown Berlin. The project will make travel more reliable, while also significantly reducing maintenance costs and the negative environmental effects resulting from the current processes for maintenance and snow removal.
- $1.3 billion for transportation investments in roads, bridges, public transit, ports, and airports, as well as electric school and transit buses, EV charging, and more.
- $155.9 million for grants, rebates, and other initiatives to accelerate the deployment of clean energy, clean buildings, and clean manufacturing. This is not inclusive of the clean energy tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- $46 million to make communities more resilient to climate change and other threats.
- $163.7 million to provide clean water across Maine and improve water infrastructure. This includes $57 million dedicated to lead pipe and service line replacement.
IIJA Funding: $44.1 million
Construction Start Date: Summer 2025
End Date: Spring 2029
With help from the federal infrastructure investment law, the Presque Isle Freight and Mobility Priority Corridor Project provides a new route for vehicles to travel around Presque Isle instead of through it. It includes construction of a 6.3-mile, two-lane road that will connect U.S. Route 1 south of the city to the current bypass section already in service. With a new interchange and overpasses, the roadway will improve freight movement as well.
Downeast Coastal US 1 Rehabilitation
IIJA Funding: $33 million
Construction Start Date: 2024
This Downeast Coastal US Route 1 Improvement Project will rehabilitate US 1 from Machias to Calais and Route 190 from Eastport to US 1 to create a consistent corridor, achieve a state of good repair, and prepare for a changing climate. Specifically, the project will rehabilitate/overlay 68 miles; widen shoulders where attainable to a minimum of 4 to 5 feet to better accommodate cyclists and pedestrians; replace drainage structures that do not have a 10-year useful life to better withstand the effects of climate change and promote fish passage; make roadside safety improvements including new guardrails, crash barriers, and rumble strips; and lay the groundwork for future EV chargers to help meet Maine’s electric vehicle plan to bring Level 3 chargers to rural Maine.
MOOSE (Maine Online Optical Statewide Enabling) Network
IIJA Funding: $30 million
Construction Start Date: July 2023
End Date: June 2025
The Maine Connectivity Authority has earned a new $30 million federal grant to improve broadband infrastructure in Maine. The competitive grant will fund 530 miles of “middle mile” infrastructure, which are regional fiber optic lines that are able to carry large amounts of data at high speeds over long distances to provide internet connectivity to homes and businesses.
“This grant will fund the construction of critical broadband infrastructure that will bring Maine closer to ensuring that anyone in Maine who wants a fast, affordable, reliable internet connection can have one. Work completed by the Maine Connectivity Authority in support of that goal positioned our state well to secure funding in what was an extremely competitive process,” Maine Governor Janet Mills said. “I thank the NTIA for its continued support of expanding connectivity in Maine, and the Maine Congressional Delegation for their work to make this funding possible.”
Downtown Sanford Village Partnership Initiative
IIJA Funding: $25 million
Construction Start Date: Summer 2026
End Date: 2030
The Downtown Sanford Village Partnership Initiative Project calls for a long-awaited revitalization of downtown Sanford by building upon numerous accomplishments the city has already made. Improvements call for replacing and/or constructing streets, sidewalks, crosswalks, underground utility ducts, streetlights, parking spaces, drainage areas, a multi-use pathway, and a Park & Ride facility primarily serving Portsmouth Naval Shipyard. Numerous safety aspects of downtown streets and sidewalks will be improved for motorists and various active transportation users. Downtown infrastructure will be modernized to attract potential employers, commercial and residential development, and prepare for a green future. This project will provide safe and efficient access to the region’s commercial center and current downtown employers, critical to Sanford’s economy and meeting Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Maine Department of Transportation standards.
- $5.1 billion for transportation investments in roads, bridges, public transit, ports, and airports, as well as electric school and transit buses, EV charging, and more.
- $330.1 million for grants, rebates, and other initiatives to accelerate the deployment of clean energy, clean buildings, and clean manufacturing. This is not inclusive of the clean energy tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- $124 million to make communities more resilient to climate change and other threats.
- $402.1 million to provide clean water across Massachusetts and improve water infrastructure. This includes $99.5 million dedicated to lead pipe and service line replacement.
IIJA Funding: $62.2 million
Construction Start Date: October 2022
End Date: June 2027
Carrying more than 175,000 vehicles per day between two of Massachusetts’ most significant roadways, interstate highways I-495 and I-90 will undergo reconstruction to reduce crashes, congestion, and travel time through the interchange. The roadways are also in a highly sensitive environment, including an Area of Critical Environmental Concern and rare species habitat, which has required striking a balance in the redesign of the interchange that would improve safety and mobility while avoiding, minimizing, or mitigating any associated impacts to sensitive resources.
Route 20 Reconstruction
IIJA Funding: $51.2 million
Construction Start Date: March 2024
End Date: November 2026
About 26,000 vehicles travel along this 3.2-mile section of Route 20 through Charlton and Oxford each day. The Massachusetts Department of Transportation is redesigning and reconstructing Route 20 in Charlton and Oxford to improve safety and traffic operations. Proposed work includes widening the roadway, replacing bridges over the Little River and the French River, adding sidewalks and shared use paths, installing a median barrier, improving safety and traffic operations at various intersections, and enhancing stormwater treatment.
Route 79-Davol Street Corridor Improvements
IIJA Funding: $46.4 million
Construction Start Date: Fall 2021
End Date: Fall 2025
The purpose of the project is to promote economic growth in Fall River by creating new developable parcels of land and to establish multimodal connectivity between the neighborhoods and the waterfront. The project combines Route 79 with northbound and southbound Davol Street, which allows the creation of 19 acres of new developable parcels, an additional nine acres of open space, the reduction of total number of travel lanes from four to two lanes in each direction, and the establishment of four cross street connections between neighborhoods and waterfront.
Andover Bridge Rehabilitations
IIJA Funding: $48.3 million
Construction Start Date: March 2024
The proposed project consists of the replacement of six bridges in the town of Andover. The replacement bridges are on I-495 north and southbound over Route 28 north and southbound, as well as I-495 north and southbound over the MBTA Railroad. Improvements on I-495 will include the reconstruction of the bridges and widening of the bridges to accommodate a future fourth lane on I-495 north and southbound. Improvements on Route 28 north and southbound under I-495 will include reconstruction of the roadway and sidewalks and providing bicycle accommodations on Route 28 in each direction. Stormwater improvements will be included as well as updated signage and pavement markings.
- $1.1 billion for transportation investments in roads, bridges, public transit, ports, and airports, as well as electric school and transit buses, EV charging, and more.
- $113.6 million for grants, rebates, and other initiatives to accelerate the deployment of clean energy, clean buildings, and clean manufacturing. This is not inclusive of the clean energy tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- $39.3 million to make communities more resilient to climate change and other threats.
- $150.7 million to provide clean water across Vermont and improve water infrastructure. This includes $57 million dedicated to lead pipe and service line replacement.
IIJA Funding: $24.8 million
Construction Start Date: 2023
End Date: 2030
The Burlington-Winooski Bridge is located between Burlington and Winooski carrying US Routes 2 and 7 over the Winooski River. This bridge provides a vital connection between the two cities, as well as the region. As the sole downtown crossing over the Winooski River, the Burlington-Winooski Bridge provides a link for approximately 25,000 vehicles per day and approximately 500 pedestrians and bicyclists per day. The overall project will include replacing the bridge and improving the intersections immediately south of the bridge, involving Riverside Street, Colchester Avenue, Mill Street, and Barrett Street. The intersection improvements will generally consist of roadway reconstruction and traffic signal modifications, with the goal of improving safety and mobility for all users.
Reconnecting Downtown Burlington
IIJA Funding: $22.4 million
Construction Start Date: 2024
This project to build two new city blocks on St. Paul and Pine Streets and to revitalize eight blocks of existing streets on Cherry and Bank Streets will establish new, direct access to public transit, reduce emissions and travel time for all modes of transportation, establish new opportunities to rebuild a once vibrant residential neighborhood lost to urban renewal, and improve economic conditions for residents in the area disproportionally impacted by the pandemic.
“The Reconnecting Downtown Burlington project is a once-in-a-generation infrastructure investment in the city of Burlington. When this project is complete, we’ll have created new opportunities to grow small businesses, build new affordable housing, and expand access to green, accessible transit in our city center,” U.S. Senator Peter Welch said. “I am so glad to see the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law come to life in such an incredible way and was proud to do my part in passing and implementing this transformative bill.”
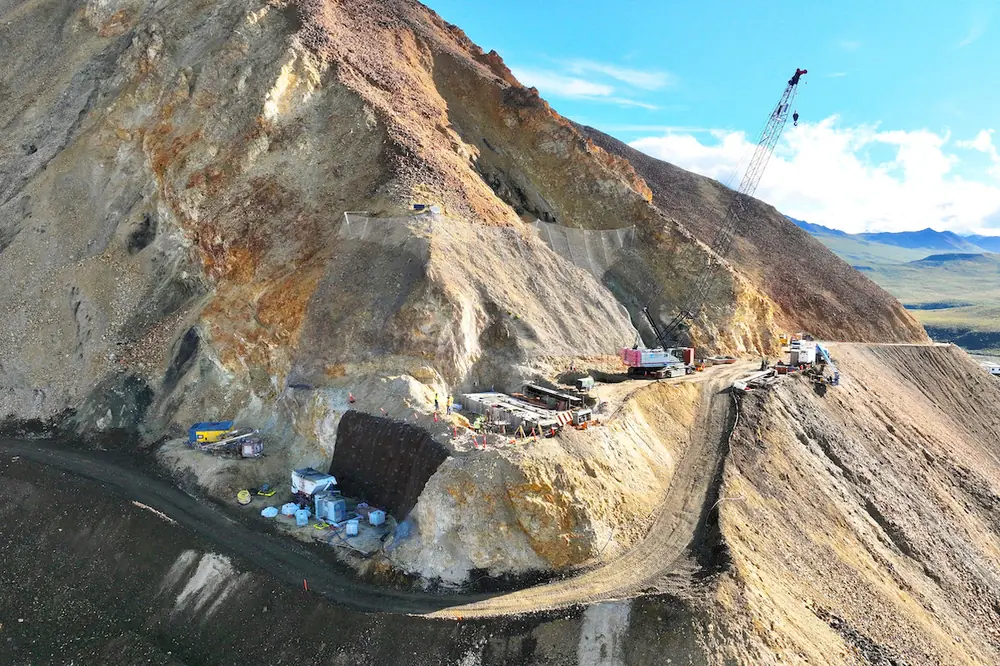
Ely Copper Mine
IIJA Funding: $29.3 million
Construction Start Date: March 2022
The Ely Copper Mine Superfund site is an abandoned copper mine located in Vershire, Orange County, Vermont. It encompasses approximately 350 acres where historic mining activities took place. The site includes about 30 acres of waste material containing an estimated 172,000 tons of waste rock, tailings, ore roast beds, slag heaps, and smelter wastes as well as more than 3,000 linear feet of underground mine workings with associated shafts and adits. No buildings remain at the site. Remnant foundations, pads, and stone walls, including a 1,400-foot-long smoke flue, demark the location of former site structures, including a former flotation mill and the smelter plant.
Brattleboro-Newfane VT30 Resurfacing
IIJA Funding: $13.6 million
Construction Start Date: June 2022
End Date: October 2023
Work will consist of milling the existing surface to a specified depth, then the first pass reclaim process will occur, pulverizing and homogenizing the remaining pavement with underlying subbase. New gravel will be placed in some areas along the corridor to improve banking, then a second pass reclaim process will take place, which will facilitate a second round of homogenizing of the gravel and pavement as well as add in a stabilizing agent to create a structural layer of subbase. Following the second pass reclaim, a structural thickness of pavement will be placed, consisting of a combination of cold mix and hot mix asphalt.